ALL-IN-ONE PLATFORM
esDynamic
Manage your attack workflows in a powerful and collaborative platform.
Expertise Modules
Executable catalog of attacks and techniques.
Infrastructure
Integrate your lab equipment and remotely manage your bench.
Lab equipments
Upgrade your lab with the latest hardware technologies.
PHYSICAL ATTACKS
Side Channel Attacks
Evaluate cryptography algorithms from data acquitition to result visualisation.
Fault Injection Attacks
Laser, Electromagnetic or Glitch to exploit a physical disruption.
Security Failure Analysis
Explore photoemission and thermal laser stimulation techniques.
EXPERTISE SERVICES
Evaluation Lab
Our team is ready to provide expert analysis of your hardware.
Starter Kits
Build know-how via built-in use cases developed on modern chips.
Cybersecurity Training
Grow expertise with hands-on training modules guided by a coach.
ALL-IN-ONE PLATFORM
esReverse
Static, dynamic and stress testing in a powerful and collaborative platform.
Extension: Intel x86, x64
Dynamic analyses for x86/x64 binaries with dedicated emulation frameworks.
Extension: ARM 32, 64
Dynamic analyses for ARM binaries with dedicated emulation frameworks.
DIFFERENT USAGES
Penetration Testing
Identify and exploit system vulnerabilities in a single platform.
Vulnerability Research
Uncover and address security gaps faster and more efficiently.
Malevolent Code Analysis
Effectively detect and neutralise harmful software.
Digital Forensics
Collaboratively analyse data to ensure thorough investigation.
EXPERTISE SERVICES
Software Assessment
Our team is ready to provide expert analysis of your binary code.
Cybersecurity training
Grow expertise with hands-on training modules guided by a coach.
INDUSTRIES
Semiconductor
Security Labs
Governmental agencies
Academics
ABOUT US
Why eShard?
Our team
Careers
FOLLOW US
Linkedin
Twitter
Youtube
Gitlab
Github
esChecker recognized in Gartner© Hype Cycle™ for Application Security, 2022
In July 2022, Gartner© released its yearly Hype Cycles™ which “provide a graphic representation of the maturity and adoption of technologies and applications, and how they are potentially relevant to solving real business problems and exploiting new opportunities” (Gartner Hype Cycle)
In its report "Hype Cycle for Application Security, 2022", Gartner© lists Mobile Application Security Testing solutions (MAST) and mentions eShard’s MAST esChecker.
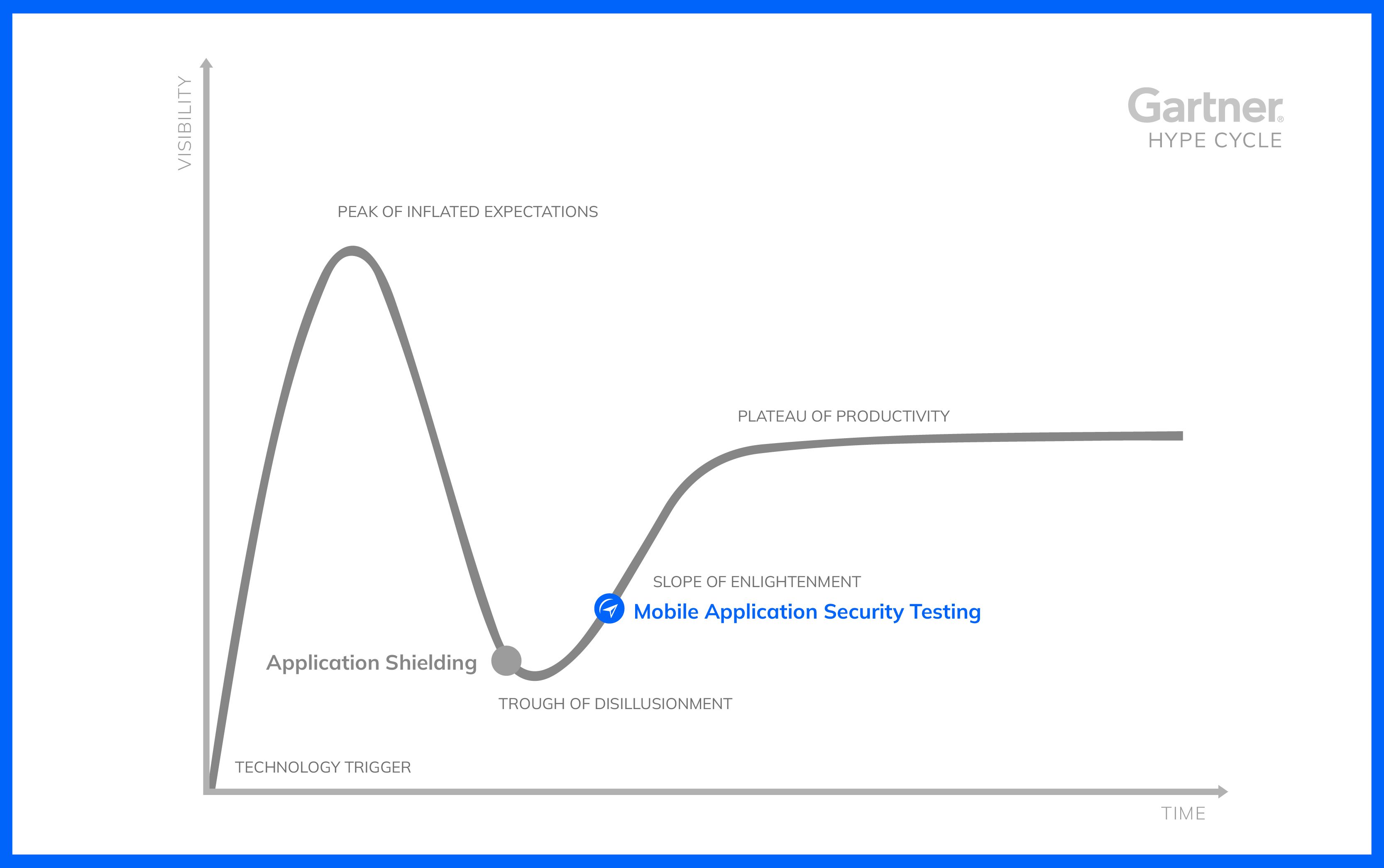
Mobile application security testing solutions can be subdivided into two technologies:
The mobile application shielding providers are maintained in the “trough of disillusionment” category. Perceived as costly, they may not be considered for hardening a mobile application yet. This could push some stakeholders to manage their own code protections. However, it is likely that maturity will grow in that space, since it requires expertise resources to keep pace with the attack techniques and the mobile platforms for a consistent protection.
And what about mobile application security testing? Inherited from the Application Security Testing space, MAST starts to create its own space. Mobile application security testing is considered as a moderate priority by Gartner®, since back-end verifications have a higher stake. MAST shall be implemented in the next 2 to 5 years, which means that you need to start working on it now!
How did we get here?
Digital transformation is ongoing for many services to the point where the most successful businesses nowadays are either built almost exclusively around their mobile application, or were required to create their own to keep up with the times.
In 2022, 91% of the global population own a mobile device, making more than 50% of the entire web traffic coming from mobile. (according to Google's latest statistics). And 72% of the fraud involves the mobile channel. This is not a surprise when looking at the customer's shift from web browser to mobile app.
The popular adoption of mobile applications comes with the trust that cyber risks have already been taken into account. But, being in the cybersecurity business for as long as I have, it's not rare to hear (sometimes from developers themselves) that protecting mobile applications is not necessary. Or it is delayed for later. And this, in spite of the fact that mobile applications are part of the digital system, the company should feel accountable for the risks. It is a bit like avoiding going to the doctor while feeling that something is wrong.
They look like normal human reactions showing resistance. Certainly because security is perceived as expensive. But also due to a lack of knowledge in the mobile hacking ecosystem.
Here are some discussions we've had in the past few months:
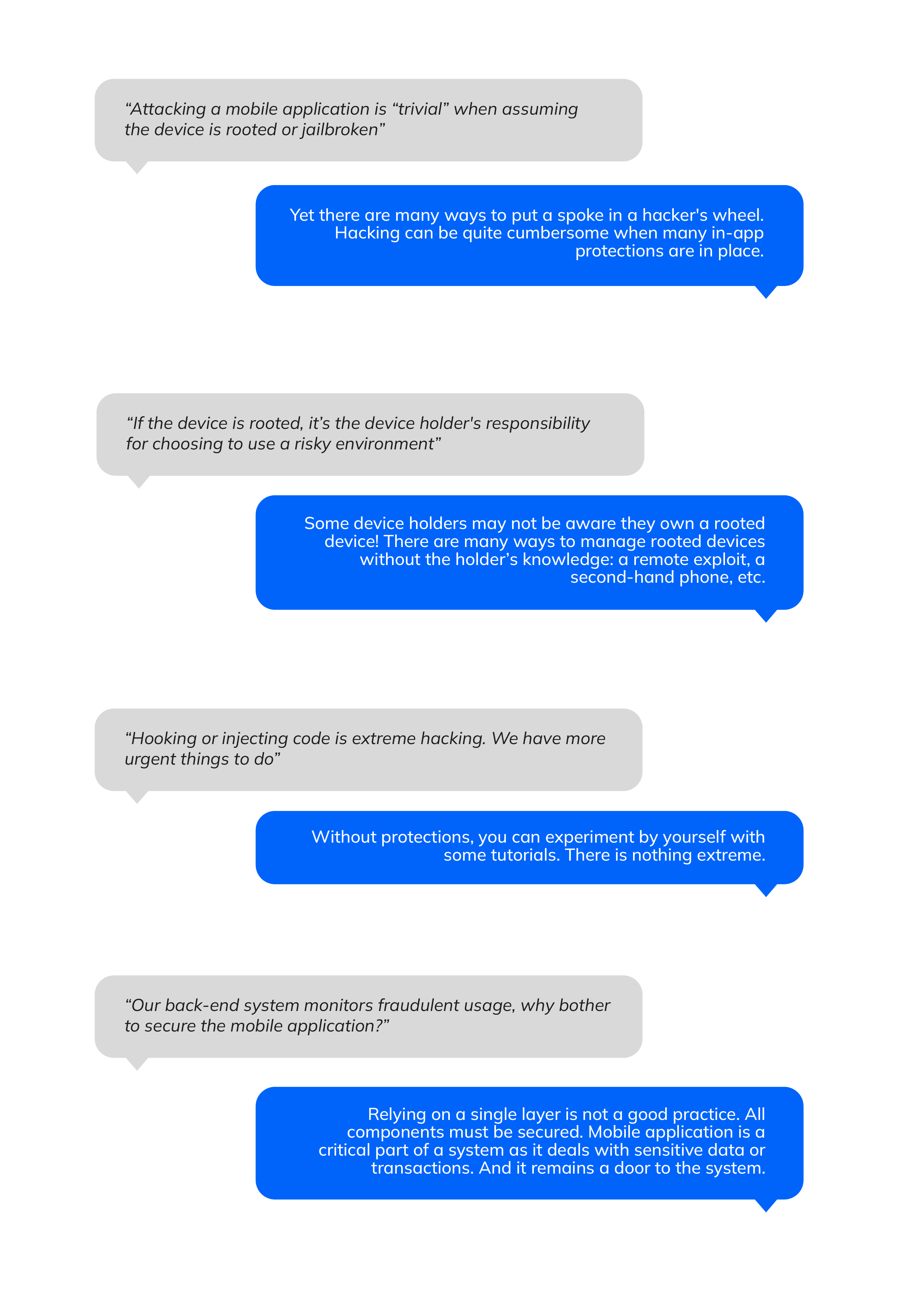
Mobile application is part of the system and therefore requires cyber assurance. Even though it is not the most critical component to secure, it deserves attention. More specifically, one has to assume that mobile applications may be executed on untrusted and unsafe devices. The exposition to reverse engineering or hacking must be considered as high.
Mobile devices represent a specific ecosystem, by both the environment execution and the attack techniques. An exploit may come out of the blue and have a sudden impact for many years. Here is a recent example on Google Pixel 6. A second example concerned Apple iPhones, when Checkra1n exploit was made public and resulted in accessible jailbreak of many phones without physical tampering.
In short, a corporate organization shall work on the assumption that:
- the mobile application binary code may fall into a hostile environment the second it is released
- their mobile application's usage will be malicious if the mobile device has resources such as hardware-based safes.
Following that line of conduct, it’s necessary to:
- Implement protections on the mobile applications, and have the back-end monitor weird behaviors;
- Protect sensitive data and transactional operations;
- Keep hackers at bay by hardening the code.
How to secure a Mobile Application?
It could be summarized in the following equation of trust:

-
Develop code with the aim to remove vulnerabilities. For this, a first layer can be managed by following good practices, like for instance those defined in OWASP MASVS. The second layer of attention would look at the so-called assets, either data value, intellectual property or transactional operations. It requires relying on the right mobile device resources or software technologies.
-
Application shielding to harden the code layers and make attack techniques more difficult. Commercial solutions implement a full range of technologies, including code obfuscation (java and or native), a RASP (Runtime Application Security Protection) or even whitebox cryptography layers. Some are available by embedding a dedicated SDK or library. Code hardening is being integrated into the compilation chain or by depackaging or repackaging techniques.
-
Quality means continuous testing. It may look obvious, but it is necessary to verify the job was properly done. When it comes to security protections, verifications can prove tricky. For instance, in order to trigger a root detection, the developer has to be in the position of testing with rooted devices. As for any other modern development process, the test must come together with the feature, without hindering the development cycle. As such, the process must be built for quick and numerous updates — test automation is a must. While DevOps has become a norm for efficient development, the Security part must be integrated for a DevSecOps chain: all security tests must be run in the CI/CD pipeline.
What is so special in the equation of trust? The ‘X” operator. If either the development, the app shielding or the quality is missing, the value is 0, resulting in a trust yielding 0. Who can afford having a 0 trust in the binary pushed on the store ?
Security verifications can be performed at the code or at the binary level. There are 10 commercial solutions identified as Mobile Application Security Testing (MAST). Indeed, testing solutions for mobile applications is specific from a technological perspective.
6 tips to choose the best MAST
Here are some tips on how to choose the best MAST tool for your mobile application.
- Pick up a tool that tests at the binary. Binary is the final code being released on the field and available to anyone. Final verifications must therefore be made at this stage of the process.
- Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST): look ahead of the marketing. Executing the code binary in real conditions is the only viable way to trigger your protections and make sure they work. This deserves a strong expertise to know how to mimic an unsafe device. You should also ask for testing evidence, like the video recording of the execution.
- Discard static-only solutions. These are simply not efficient enough. Static testing is quickly blind when code obfuscation is applied. And tools do not necessarily cope with all development frameworks (Xamarin, Hermes, …).
- OWASP is your reference. OWASP plays a huge role in the Mobile Application Testing world. They keep contributing to this expertise and a good testing tool should refer to their testing guide (OWASP MSTG). If the solution you’re targeting refers only to OWASP Mobile Top 10, consider it as immature. It was never supposed to be a standard, it is only a list of risks.
- Look at the false positive. False positives create confusion and a lack of peace of mind. Being able to check the results yourself with confidence is essential when choosing a testing solution. If you can't, run away from black-box solutions.
- Pentesting is NOT a quality process. A pentesting explores how much a solution can be broken in a given time. This is valuable to stress your system and identify potential vulnerabilities. However, only a MAST tool provides assurance about the code quality and prevents avoidable regressions.
eShard is proud to share that esChecker has been listed by Gartner© to be a leading edge MAST solution. One of the few taking the mobile application binary as input. This is the final check before the application goes live.

