ALL-IN-ONE PLATFORM
esDynamic
Manage your attack workflows in a powerful and collaborative platform.
Expertise Modules
Executable catalog of attacks and techniques.
Infrastructure
Integrate your lab equipment and remotely manage your bench.
Lab equipments
Upgrade your lab with the latest hardware technologies.
PHYSICAL ATTACKS
Side Channel Attacks
Evaluate cryptography algorithms from data acquitition to result visualisation.
Fault Injection Attacks
Laser, Electromagnetic or Glitch to exploit a physical disruption.
Photoemission Analysis
Detect photon emissions from your IC to observe its behavior during operation.
EXPERTISE SERVICES
Evaluation Lab
Our team is ready to provide expert analysis of your hardware.
Starter Kits
Build know-how via built-in use cases developed on modern chips.
Cybersecurity Training
Grow expertise with hands-on training modules guided by a coach.
ALL-IN-ONE PLATFORM
esReverse
Static, dynamic and stress testing in a powerful and collaborative platform.
Extension: Intel x86, x64
Dynamic analyses for x86/x64 binaries with dedicated emulation frameworks.
Extension: ARM 32, 64
Dynamic analyses for ARM binaries with dedicated emulation frameworks.
DIFFERENT USAGES
Penetration Testing
Identify and exploit system vulnerabilities in a single platform.
Vulnerability Research
Uncover and address security gaps faster and more efficiently.
Code Audit & Verification
Effectively detect and neutralise harmful software.
Digital Forensics
Collaboratively analyse data to ensure thorough investigation.
EXPERTISE SERVICES
Software Assessment
Our team is ready to provide expert analysis of your binary code.
Cybersecurity training
Grow expertise with hands-on training modules guided by a coach.
INDUSTRIES
Semiconductor
Automotive
Security Lab
Gov. Agencies
Academics
Defense
Healthcare
Energy
ABOUT US
Why eShard?
Our team
Careers
FOLLOW US
Linkedin
Twitter
Youtube
Gitlab
Github
The Side Channel Chronicles #2: Getting started
I vividly remember my first attempt at capturing side channels from a device. As a cryptologist with no experience in electronics, facing an oscilloscope for the first time was daunting. Fortunately, a microelectronics engineer from the Wireless team guided me.
“Tell me what you're looking for, and I'll tell you how to find it,” he said.
Our initial session was eye-opening. I spent a lot of time explaining what side channels are and how tiny currents or timing delays could reveal secret data processed by the device. Through this process, I learned there are numerous ways and vectors to obtain this critical leaking information.
In this series, I’m going to share the essential information I collected on side channel attacks since that day.
Getting started with Side Channel
There are various tools for capturing side-channel information from electronic devices, each with different levels of noise and precision. Side-channel observations can be performed using different types of probes: voltage, current, passive, differential, and even electromagnetic probes.
Some methods require device modification, such as inserting a resistor in series with the ground, while others might involve simply wrapping an alimentation wire or using an antenna with an amplifier to capture electromagnetic field variations.
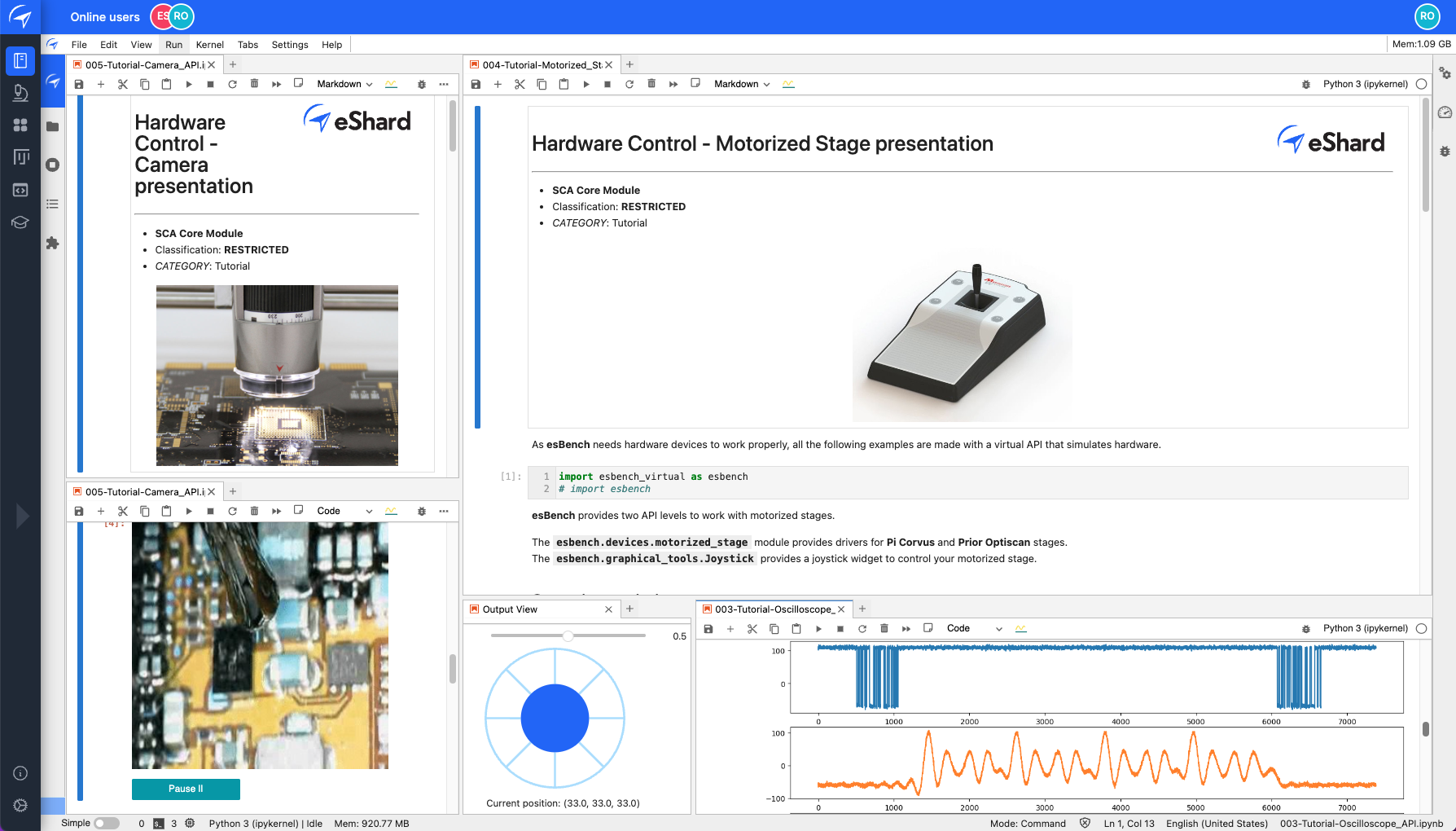 Overview of bench control set up in esDynamic
Overview of bench control set up in esDynamic
Access and Preparation
The first major lesson was the importance of access and preparation according to the target device and desired side-channel. Whether targeting a specific circuit part or the overall activity, the appropriate preparation is crucial.
Simple methods include inserting a resistor in series with the circuit ground, while more complex methods may involve chemical and mechanical preparations for tiny electromagnetic probes. For timing attacks, a passive voltage probe on the communication signal and oscilloscope measurements can be effective. For more detailed observations, a differential probe to measure power consumption is beneficial.
Measurement Effects
Another critical lesson involved understanding the impact of the power supply on signal quality. Noise from the power source can significantly affect the Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR). Starting with a stable power supply and using isolation techniques, like power decoupling, are essential for clean side-channel traces.
Additionally, synchronization between the device's clock, communication clock, and oscilloscope sampling clock is vital to reduce jitter and improve accuracy. Methods to align and synchronize these clocks are important to mitigate noise from asynchrony.
Environmental Effects
Environmental factors, like temperature, pressure, and humidity, also impact long-duration acquisition campaigns. I discovered that room temperature variations could affect trace quality. For example, nighttime acquisitions in a stable environment differ from daytime ones influenced by human activity. It's important to normalize traces or control environmental conditions to mitigate these effects.
Another challenge is electromagnetic interference from nearby electronic devices, particularly mobile phones. Such interference can introduce noise into your acquisition. For short acquisitions, this noise is detectable, but for longer campaigns, turning off devices or using a Faraday cage can help.

Let’s get practical: Acquisition
How to use an Oscilloscope
The first practical step in side channel attacks is setting up an oscilloscope. An oscilloscope is an electronic instrument that visualizes and measures electrical signals, displaying voltage changes over time on a screen. It is essential for analyzing the performance of electronic devices and capturing detailed signal traces.
Operating an oscilloscope for side-channel analysis involves several key steps:
1️⃣ Set Channels Correctly: Ensure the channels are configured according to the connected probes, paying special attention to impedance settings. Proper channel setup is crucial for accurate signal capture.
2️⃣ Choose the Appropriate Sampling Rate: Balance between too low a rate, which can cause aliasing, and too high a rate, which can create unnecessary data points. An optimal sampling rate ensures you capture all relevant signal details without excess data.
3️⃣ Maximize the Range: Utilize the oscilloscope’s resolution effectively by capturing the signal within an appropriate voltage range. This ensures that the entire signal is within view, maximizing the device’s resolution capabilities.
An important element in trace processing and synchronization is the trigger capability. Effective triggering can significantly lower post-processing steps and reduce the size of your acquisition. Ideally, you want to capture only the signal of interest. For this, use a stable trigger before the activity starts, such as a rising edge on an I/O or an identifiable pattern, and another trigger to stop acquisition, like a falling edge on an I/O after the activity. This method helps you focus on meaningful information and reduces irrelevant data.
Advanced triggering techniques can further enhance your analysis. Most oscilloscopes offer a sequence mode, allowing efficient capture of multiple successive events with minimal delay. This technique, combined with dedicated software operated by the Device Under Test (DUT), can significantly reduce the number of acquisitions needed for complex tasks like breaking a hardware AES. However, such extensive data collection is rarely necessary for most devices.
Signal Processing and Post-Processing
Once you have captured the results with the oscilloscope, post-processing becomes crucial. Classical post-processing can reveal signal characteristics that aid in key recovery. Many oscilloscopes come with built-in signal processing tools, which can be used to better understand your side-channel data.
Techniques like filtering, auto-correlation, demodulation, and spectrograms can significantly enhance your understanding and the quality of your setup. We will delve deeper into these techniques in future blog posts.
Effective side-channel analysis requires balancing acquisition speed, signal quality, and post-processing. This involves:
- Speed: Optimizing communication with the device and oscilloscope, and utilizing advanced triggering techniques.
- Quality: Ensuring that the oscilloscope and entire acquisition chain are well-prepared and stable.
- Processing: Understanding and managing various types of noise and signals.
Practical experience can get you far
Lastly, setting up an effective side-channel analysis requires experience, and it's crucial to leverage that expertise. To ensure we make the most of our experience, we meticulously document our acquisition campaigns. This documentation includes detailed explanations and code in notebooks, making the acquisition setup, the scenarios used to trigger victim operations, and the data acquisition process clear and understandable. This thorough documentation allows anyone to replicate, set up, and conduct new acquisition campaigns with similar results, ensuring consistency and reliability in our side-channel analysis.
At eShard, we offer not only the tools to support your side-channel campaigns but also our extensive expertise. Our resources include an extensive collection of executable and customizable use cases, tutorials, theoretical notebooks, and practical experience through starter kits and hands-on cybersecurity training with our experts.
Stay tuned for the next "The Side Channel Chronicles," where we will dive deeper into advanced techniques and tools to further your understanding and capabilities in side-channel analysis.
